Physical Chemistry - Chemical Equilibrium
Complete Chemistry for Engg and Medical Entrance Exam Preparation. ( IIT JEE Main | Advanced | BITSAT | SAT | NEET etc.)

What you will learn
Identify dynamic nature of equilibrium involved in physical and chemical processes
State the law of equilibrium
Explain characteristics of equilibria involved in physical and chemical processes
Write expressions for equilibrium constants
Establish a relationship between Kp and Kc
Explain various factors that affect the equilibrium state of a reaction
Why take this course?
SUMMARY
When the number of molecules leaving the liquid to vapour equals the number of molecules returning to the liquid from vapour, equilibrium is said to be attained and is dynamic in nature. Equilibrium can be established for both physical and chemical processes and at this stage rate of forward and reverse reactions are equal. Equilibrium constant, Kc is expressed as the concentration of products divided by reactants, each term raised to the stoichiometric coefficient.
Equilibrium constant has constant value at a fixed temperature and at this stage all the macroscopic properties such as concentration, pressure, etc. become constant. For a gaseous reaction equilibrium constant is expressed as Kp and is written by replacing concentration terms by partial pressures in Kc expression. The direction of reaction can be predicted by reaction quotient Qc which is equal to Kc at equilibrium. Le Chatelier’s principle states that the change in any factor such as temperature, pressure, concentration, etc. will cause the equilibrium to shift in such a direction so as to reduce or counteract the effect of the change. It can be used to study the effect of various factors such as temperature, concentration, pressure, catalyst and inert gases on the direction of equilibrium and to control the yield of products by controlling these factors. Catalyst does not effect the equilibrium composition of a reaction mixture but increases the rate of chemical reaction by making available a new lower energy pathway for conversion of reactants to products and vice-versa.
Screenshots

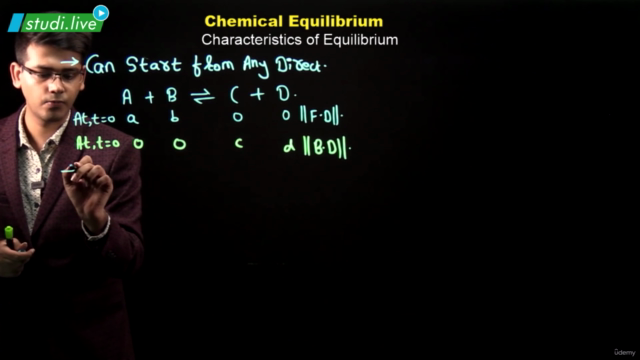
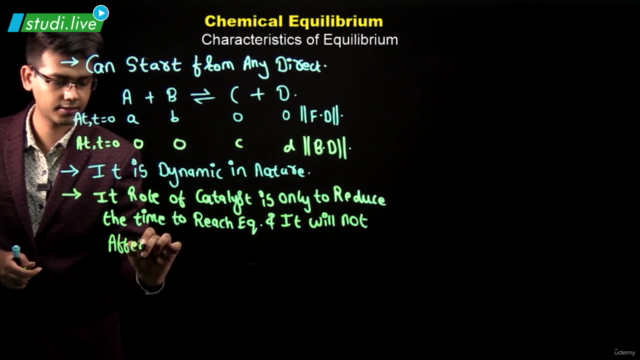

Charts
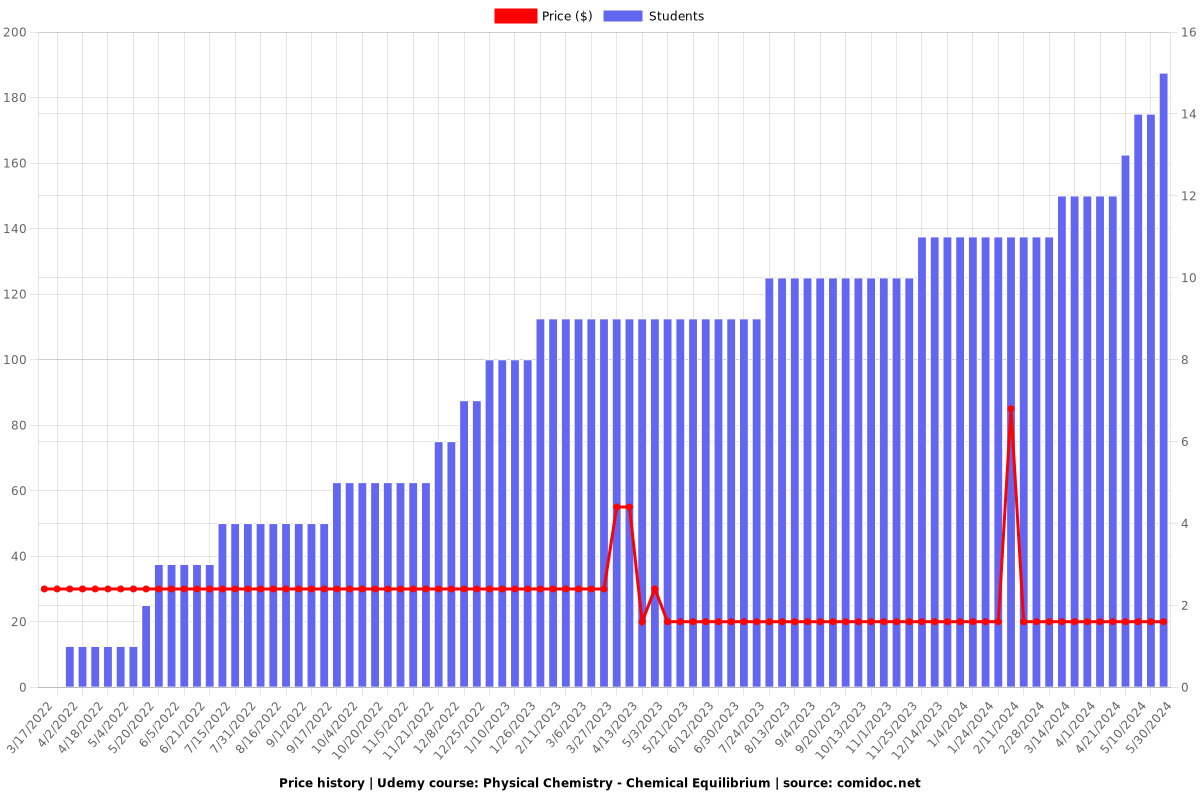
Price
Rating
Enrollment distribution