Corporate Finance Management - From Beginner to Advanced
Types of Financing, Ratio Analysis, Time Value of Money, Cost of Capital, Capital Structure, Leverage, Capital Budgeting

What you will learn
Understand Meaning and Concepts of Finance Management
Identify and understand different Sources of Finance and Types
Types of Long Term and Medium Term finance
Types of Equity Share Capital and Preference share capital
What is Debentures/ Bonds ? Types of Debentures and Bonds
Venture Capital Financing
Asset Securitisation
Lease Financing - Explanation of concept and types of lease
Depository Receipts - ADR (American Depository Receipts), GDR (Global Depository Receipts) , IDR (Indian Depository Receipts))
Trade Credit
Accrued Expenses
Deferred Income and advance from customers
Short Term Bank advances and its types
Bridge Financing
Commercial Paper
Treasury bills and Certificate of Deposits
Different Types of Financial Ratios - Calculation and Analysis along with illustrations
Types of Liquidity Ratios / Short Term solvency Ratios - Calculation and analysis along with illustrations
Current Ratios
Quick Ratio / Acid Test Ratio
Cash Ratio / Absolute Liquidity Ratio
Interval Measure Ratio
Types of Leverage Ratios / Long Term solvency ratios - Calculation and analysis along with illustrations
Equity Ratios
Debt Ratio
Debt To Equity Ratios
Debt To Total Assets ratios
Proprietary Ratio
Capital Gearing Ratio
Debt Service Coverage Ratio
Dividend Coverage Ratio
Interest Coverage Ratio
Fixed Charges Coverage Ratio
Types of Activity Ratios / Turnover Ratios/ Efficiency Ratios / Performance Ratios - Calculation and analysis along with illustrations
Total Assets Turnover Ratio
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio
Net Assets Turnover Ratio
Current Assets Turnover Ratio
Working Capital Turnover Ratio
Inventory Turnover Ratio
Receivables Turnover Ratio
Payables Turnover Ratio
Profitability Ratios - Calculation and analysis along with illustrations
Gross Profit Ratio
Net Profit Ratio
Operating Profit Ratio
Expenses Ratio - COGS Ratio, Office and Administration Expenses Ratio, Selling and Distribution Expenses Ratio, Operating Expenses Ratio
Return on Investment (ROI)
Return on Asset (ROA)
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
Return on Equity (ROE)
DuPont Analysis on ROI, ROA and ROE
Earning Per Share (EPS)
Dividend Per Share (DPS)
Dividend Payout Ratio
Price Earning Ratio
Dividend and Earning Yield Ratio
Market Value by Book Value (MVBV)
Q ratio
Time Value of Money - Concept and Use of Time value of Money
Simple Interest and Power of Compounding
Present Value and Future Value of Single Cash Flow
What is Annuity and Types of Annuity
Present Value and Future Value of Annuity
Annuity Factor and Discount Factor
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
Cost of Capital
Cost of Redeemable and Irredeemable Debts
Cost of Zero Coupon Bonds using IRR method
Cost of Ammortised Bonds using IRR Method
Methods to Calculate cost of Equity
Gordon's Growth Model
Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
Cost of Preference Shares
Weighted average cost of Capital
Marginal Cost of Capital
What is Leverage ?
Operating Leverage, Financial Leverage and Combined Leverage
Break even Analysis- Operating Break even Point and Financial Break even point
Margin of Safety and Operating Leverage
Financial Leverage - Trading on Equity
Financial Leverage - Double edge Sword
Capital Structure Meaning and Theories
Net Income Approach
Traditional Approach
Net Operating Income Approach
Modigliani and Miller Approach
Arbitrage - Meaning and illustrations
Trade off Theory
Pecking Theory
EBIT- EPS - MP analysis
Return on Asset , Fixed Costs and EPS analysis
Financial Break even analysis
Indifference Points
Over Capitalisation and Under Capitalisation
Capital Budgeting - Meaning and Process
Types of Capital Investment decisions
Replacement and Modernization decision
Expansion Decision
Diversification Decision
Mutually Exclusive Proposals Decision
Accept or Reject Decision
Contingent Decision
Difference between Accounting Profit and Cashflow
Meaning of Incremental Cashflows
Depreciation and Tax Benefit on Depreciation
Opportunity Cost and Sunk Cost
Working Capital Cost
Allocated Overhead costs
Types of Cashflow for New Projects and Replacement Projects
How to Calculate Cashflows
Block of Assets and Depreciation Principle
Treatment of Financing Costs
Post Tax Principles
Capital Budgeting Techniques
Payback Period Method - Meaning, Illustrations advantages and Disadvantages
Payback Period Reciprocal Method
Accounting Rate of Return Method (ARR) - Meaning, Illustrations advantages and Disadvantages
Discounted Payback Period Method - Meaning, Illustrations advantages and Disadvantages
Profitability Index Method (PI) - Meaning, Illustrations advantages and Disadvantages
Net Present Value Method (NPV) - Meaning, Illustrations advantages and Disadvantages
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) - Meaning, Illustrations advantages and Disadvantages
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) and Net Present Value Method (NPV) Reinvestment Assumption
Multiple Internal Rate of Return (Multiple IRR)
Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) - Meaning, Illustrations advantages and Disadvantages
Capital Rationing
Divisible and Non- Divisible Projects
Methods to analyze Mutually Exclusive Projects with different tenures
Replacement Chain Method
Equivalent Annualized Criterion Method
Risk analysis in Capital Budgeting
Project Specific Risk
Company Specific Risk
Industry Specific Risk
Competition risk
Risk due to economic factors
International risk
Market risk
Types of Risk Analysis Techniques
Risk Analysis Technique - Statistical Technique - Probability
Risk Analysis Technique - Statistical Technique - Standard deviation and Variance
Risk Analysis Technique - Statistical Technique - Coefficient of Variation
Risk Analysis Technique - Conventional Technique - Risk adjusted discount Rate
Risk Analysis Technique - Conventional Technique - Certainty Equivalent
Risk Analysis Technique - Sensitivity Analysis
Risk Analysis Technique - Scenario Analysis
Dividend decisions - Introduction and significance
Forms of Dividend - Cash Dividend and Bonus Shares (Stock Dividend)
Relationship between Retained earnings and Growth
Factors affecting Dividend decisions
Dividend Policy - Mature Company and Growth Company
Theories of Dividend Policy
Modigliani and Miller Hypothesis
Walter's Model
Gordon's Growth Model
Dividend Discount Model
Graham and Dodd Model
Linter's Model
Stock Splits
Meaning ,Significance and Types of Working Capital
Optimum Working Capital
Approaches for Working Capital Investment
Working Capital Cycle or Operating Cycle - Concept and calculation
Raw Material Storage Period
Work in Progress holding period
Finished Goods Storage Period
Receivables Collection Period
Payables Period
Working Capital Estimation
Working Capital on Cash cost basis
Impact of Double Shift on Working Capital
Treasury and Cash Management
Cash Budget
Accelerating Cash Collections and Controlling Payments
Cash Management Models
William J Baumol EOQ Model
Miller Orr Cash Management Model
Management of Marketable securities
Inventory Management Basics
Reorder Level
Reorder Quantity
Minimum Stock Level
Maximum Stock Level
Average Stock Level
Danger Level and Buffer Stock
Management of Debtors - Meaning and Objective
Factors determining Credit Policy
Approaches to evaluation of credit policies - Total Approach and Incremental Approach
Financing Receivables
Factoring Services evaluation
Forfaiting
Management of Payables and Cost of Payables
Working Capital Finance
Spontaneous Sources of Finance
Inter Corporate Loans and Deposits
Commercial Papers
Bills Discounting, Rediscounting and Factoring
Forms of Bank Credit
Why take this course?
Hi
This is a Corporate Financial management course from beginners to advanced level. It begins with understanding basic concepts and terms of financial management to application of the financial management in decision making. The course consists of video lectures along with solved illustrations and Quiz that provides better understanding of concept. It is logically divided into various Sections :
Module 1 : Introduction
(Includes Section 1)
Introduction and understanding the meaning of financial management.
Module 2 : Sources of Finance
(From Section 2 to Section 6)
Here we are identifying and understanding different sources of Finance. This includes all long term finance and medium term finance such as Equity and Preference share capital , Bonds and Debentures, Venture Capital, Asset Securitization, Lease Financing, Depository Receipts, Trade Credit and accrued expenses. It also includes all short term finance such as Bridge Finance, Treasury Bills, Certificate of Deposits, Commercial paper etc. All the sources of finance are explained in video lectures along with illustrations.
Module 3 : Financial Ratios and Analysis
(From Section 7 to Section 11)
Here We discuss about different types of Financial Ratios such as Liquidity Ratios (Short term solvency ratios) , Leverage Ratios (Long Term solvency ratios) ,Activity Ratios (Turnover ratios) and Profitability Ratios.
Liquidity Ratios includes current ratio, quick ratio, cash ratio and Interval measure ratio. Each ratio is explained in video lecture along with illustrations.
Leverage Ratios include equity ratio, debt ratio, debt to equity ratio, debt to total assets ratio, proprietary ratio, capital gearing ratio, debt service coverage ratio, dividend coverage ratio, interest coverage ratio, fixed charges coverage ratio etc. Each ratio is explained in video lecture along with illustrations.
Turnover ratios include fixed assets turnover ratio, net assets turnover ratio, current assets turnover ratio, working capital turnover ratio, inventory turnover ratio, receivables turnover ratio, payables turnover ratio etc. Each ratio is explained in video lecture along with illustrations.
Profitability ratios include gross profit ratio, net profit ratio, operating profit ratio, expenses ratio, return on assets, return on capital employed, return on equity, earning per share, dividend per share, dividend payout ratio, price earning ratio, dividend and earning yield ratio, market value by book value ratio, Q ratio. Each ratio is explained in video lecture along with illustrations.
DuPont Analysis on ROI (Return on Investment) , ROA (Return on Assets) and ROE (Return on Equity)
This module also includes a comprehensive solved illustration that explains how to calculate all types of ratios and how to use these ratios for analysis and decision making.
Module 4 : Time Value of Money
(From Section 12 to Section 15)
Here we discuss about the concept of Time Value of Money and how to use concept of time value of money. The relationship between inflation, purchasing power and Time value of money is separately discussed. Other topics included are Difference between Simple interest and compound interest, Present value and Future value of money, Formula for present value and future value, Discount Factor, Annuity, Present Value and Future Value of Annuity. All topics are explained in video lecture along with examples.
Module 5 : Cost of Capital
(From Section 16 to Section 19)
Here we will learn how to calculate cost of capital for individual capitals i.e Cost of Debentures/ Bonds, Cost of Preference shares , Cost of Equity shares and then How to calculate total cost of capital.
Cost of debt/Bonds and debentures includes calculation of Cost of Redeemable and Irredeemable debts using approximation method and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Method. It also includes separate lecture wherein logic for using current price in calculating cost of capital is explained.
Cost of Preference shares using Approximation method and Internal Rate of Return (IRR Method)
Cost of Equity and Retained Earnings using Dividend Price Model, Earnings Approach model, Gordon's growth model, Realized Yield Approach, Capital Asset Price Model is explained along with examples. Besides Calculation of Growth Rate for Gordon's growth model, Beta , Types of Risks - Systematic and Unsystematic risks are explained in separate video lecture along with examples.
This section is concluded by calculating weighted average cost of capital (WACC) and Marginal cost of capital.
Module 6 : Leverages
(From Section 20 to Section 23)
Here we will be learning about different types of Leverages - Operational Leverage, Financial Leverage and Combined Leverage. This will be followed by Formula to calculate degree of operating leverage (DOOL/DOL), degree of Financial leverage (DOFL/DFL) and degree of combined leverage (DOCL/DCL). Operating and Financial break even points are analyzed in separate lectures and relationship of break even points with leverage is discussed. Some other topics include relationship between Margin of Safety and Operational leverage, Relationship between Break even point - Fixed cost and operational leverage, Why financial leverage is known as trading on equity and double edge sword.
Module 7 : Capital Structure
(From Section 24 to Section 33)
It includes meaning of capital structure and capital structure theories. Following theories are discussed in this module : Net Income approach, Traditional Approach, Net Operating Income approach, Modigliani and Miller approach , Trade off theory and pecking theory. Along with this following topics are also discussed - meaning of arbitrage with solved illustrations, Indifference points, Over capitalization and under capitalization.
Module 8 : Capital Budgeting
(From Section 34 to Section 49)
It begins meaning of Capital Budgeting and purpose of Capital Budgeting. This is followed by process of capital budgeting and types of Capital budgeting decisions - Replacement and Modernization decisions, Expansion decisions, Diversification decisions, Mutually Exclusive decisions, Accept or Reject decision, Contingent decision.
Other terms such as incremental cashflows, Tax Benefit on Depreciation, Opportunity cost and Sunk cost, Working capital costs, allocated overhead costs are also explained in separate tutorials along with illustrations. This is followed by types of cashflows for new project and replacement project along with basic principles of calculating cashflows.
All Capital Budgeting Techniques i.e Payback Period Method, Payback Reciprocal Method, Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) Method, Discounted Payback period method, Profitability Index method (PI) , Net Present Value Method (NPV) , Internal Rate of Return Method (IRR) and Modified Internal Rate of Return (MIRR) are discussed in detail along with meaning , Illustrations , advantages and disadvantages. Reinvestment assumptions and anomalies in Net Present Value Method (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return Method (IRR) method along with reasons and examples are discussed separately.
Capital Rationing Meaning and Capital Rationing for Divisible and Indivisible projects is discussed along with solved illustrations.
Methods to analyze Mutually exclusive projects with different tenures - i.e Replacement chain Method and Equivalent annualized criterion method are also included along with solved examples.
Module 9 : Risk Analysis in Capital Budgeting
(From Section 50 to Section 55)
It begins with different types of risks involved in capital budgeting. This includes Project Specific risk, Company Specific risk, Industry Specific risk, Competitive risk, Market risk, Risk due to economic factors and International risk.
The following techniques of Risk analysis are explained along with example in separate video lectures :
Statistical Technique - Probability
Statistical Technique - Variance and Standard Deviation
Statistical Technique - Coefficient of Variation
Conventional Technique - Risk adjusted discount rate
Conventional Technique - Certainty Equivalents
Sensitivity Analysis
Scenario Analysis
Module 10 : Dividend Decisions
(From Section 56 to Section 62 )
It begins with the introduction on dividend decisions that includes separate video lectures on Significance of Dividend decisions, Forms of Dividend, Relationship between Retained Earnings and Growth, Factors affecting dividend decisions, Dividend Policies and types , Dividend policies for mature companies and growth companies.
It is followed by explanation of following theories of Dividend Policy :
Modigliani and Miller Hypothesis
Walter's Model
Gordon's Model
Dividend Discount Model - No Growth, Constant Growth and Variable Growth
Graham and Dodd Model
Linter's Model
Each Theory consists of video lectures explaining assumptions, formula , solved illustrations , advantages and limitations.
The module ends with explanation of Stock Splits.
Module 11 : Working Capital
(From Section 63to Section 70 )
This module begins with meaning significance and types of working capital.
The other sections includes following topics :
Optimum working capital
Operating Cycle and Working Capital Cycle - Meaning, Concept and Calculation along with comprehensive solved example
Estimation of Working Capital in detail that includes estimation of each and every component of working capital along with solved illustration.
Working Capital on Cash cost basis- Meaning, Concept and Calculation along with comprehensive solved example
Impact of Double Shift on Working Capital - Meaning, Concept and Calculation along with comprehensive solved example
Module 12 : Treasury and Cash Management
(From Section 71 to Section 75 )
It begins with meaning of Cash management along with functions of Treasury and Cash Management. It is followed by preparing of Cash Budgets - Both for long term and Short term along with solved illustrations.
Further it is followed by Cash Management Models and Theories. It includes William J Baumol's EOQ Model and Miller Orr Cash Management model.
It ends with lectures on recent developments in Cash Management Systems and Management of Marketable securities.
Module 13 : Inventory Management
(Section 76)
This includes various topics related to Inventory management such as Reorder Level, Reorder Quantity, Minimum stock level, average stock level , Maximum stock level, Danger level and buffer stock along with solved illustration on inventory management.
Module 14 : Management of Receivables and Payables
(From Section 77 to Section 81)
This module includes following topics :
Management of Debtors - Meaning and Objectives
Credit Policy - Meaning and Factors affecting credit policy
Approaches to evaluation of Credit policies along with the solved illustrations- Evaluation of Credit policies on Total Approach and Evaluation of Credit policies on Incremental Approach.
Financing receivables
Factoring services
Forfaiting
Innovations in receivables management
Monitoring of receivables
Management of Payables
Cost of Payables - Calculation along with solved illustration
Module 15 : Working Capital Finance
(Section 82)
This module includes following topics :
Meaning an types of Working capital Finance
Spontaneous working capital finance
Intercorporate debts and deposits
Commercial Papers
Bills discounting, Rediscounting and Factoring
Forms of Bank credit for working capital finance
Thus, this course provides complete understanding about basics of Corporate Finance or Management Finance. Hope you enjoy it.
Tip : It is better to solve illustrations along with lectures for better understanding of concept.
Happy Learning !
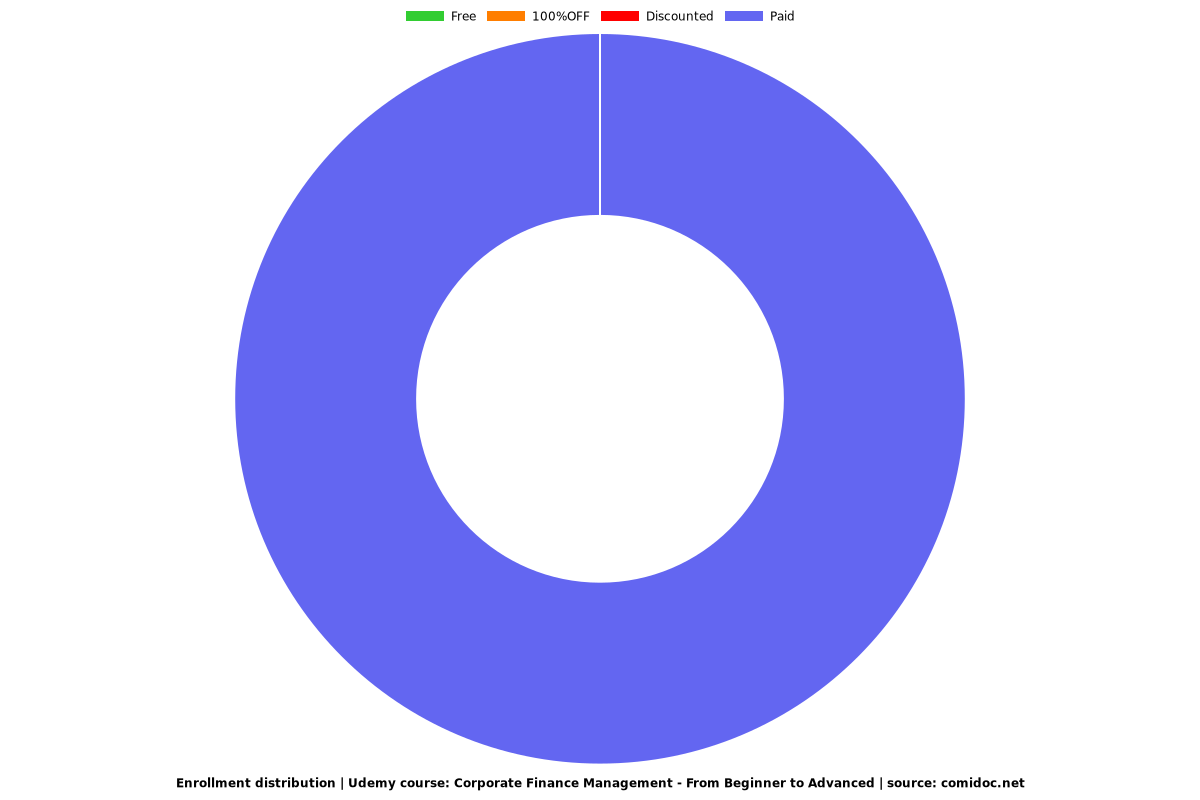
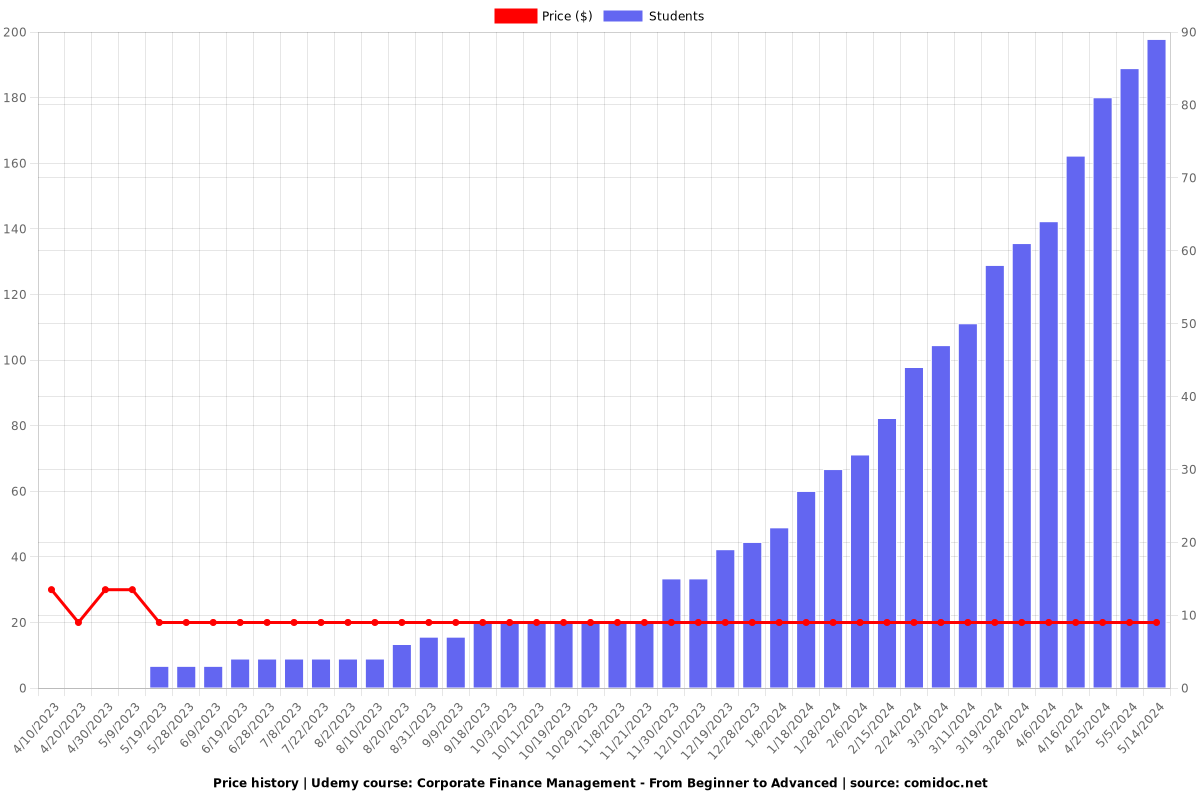
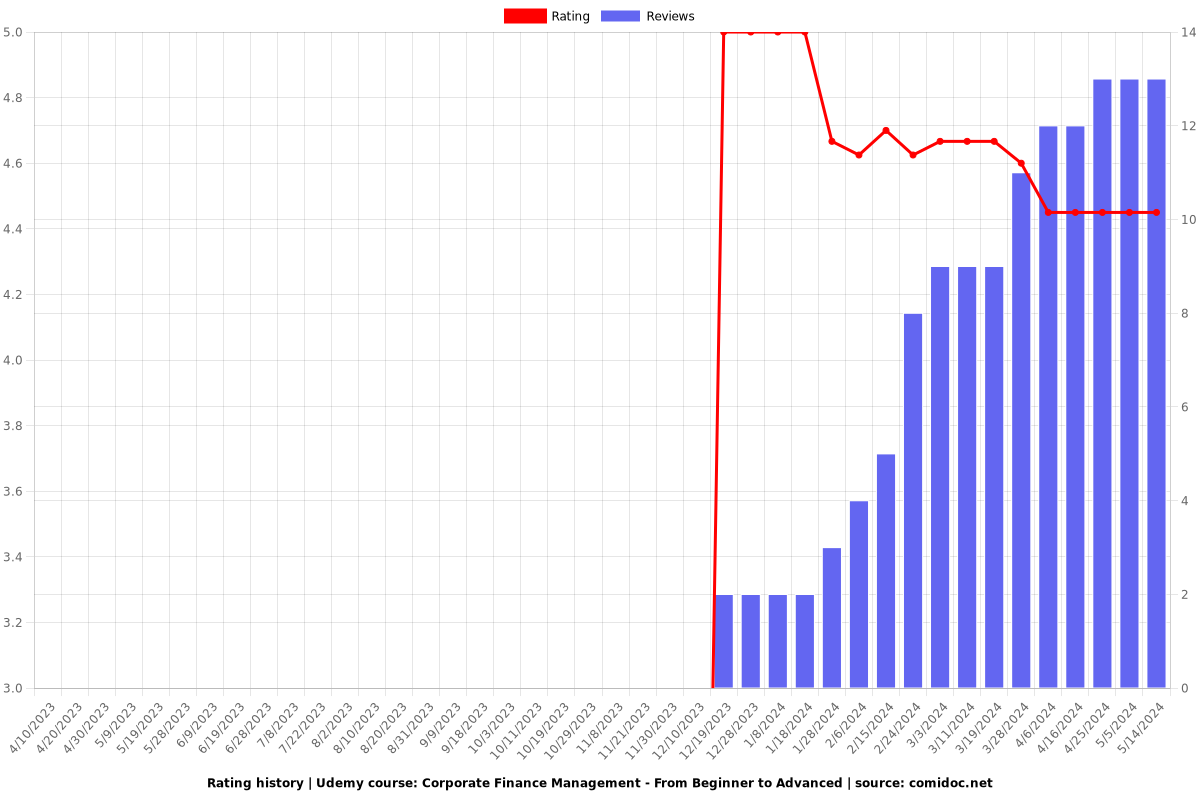
Charts
Price
Rating
Enrollment distribution