Digital Safety: Cyber Security Essentials & Myths
Gaining Expertise in Online Protection
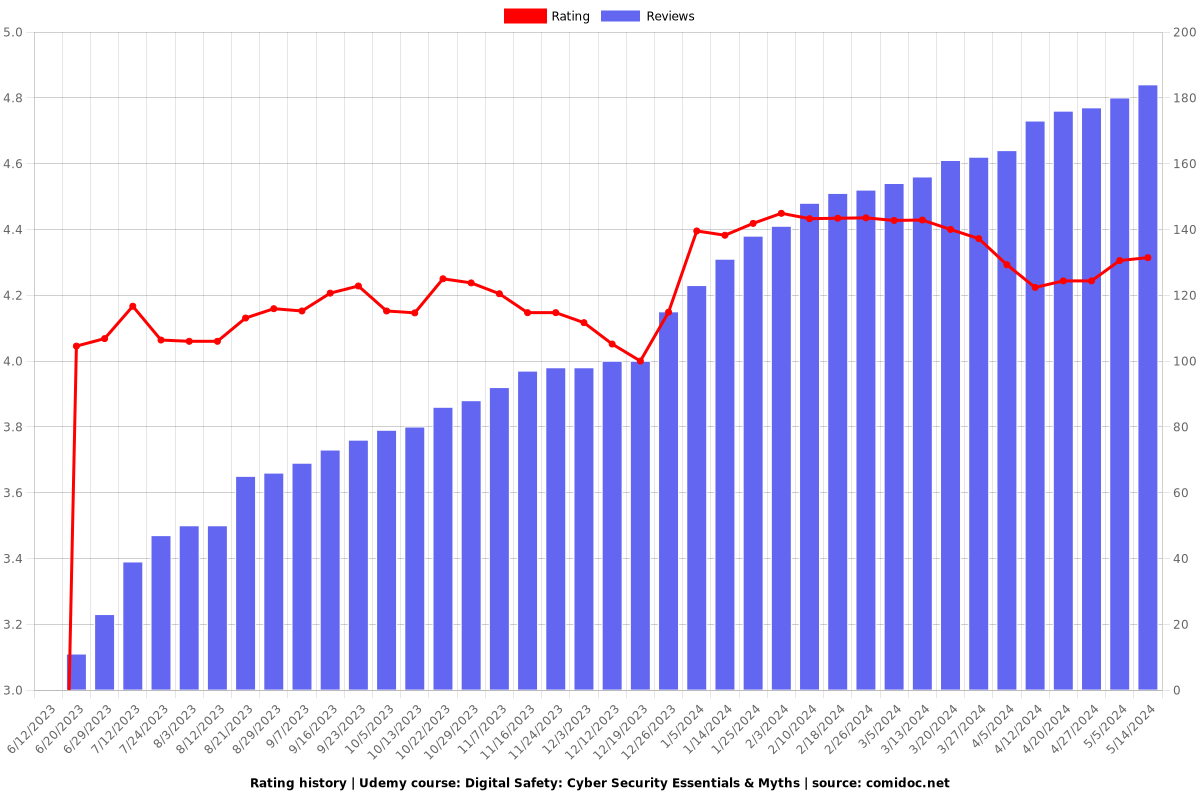
4.31 (184 reviews)

15,424
students
4 hours
content
Mar 2024
last update
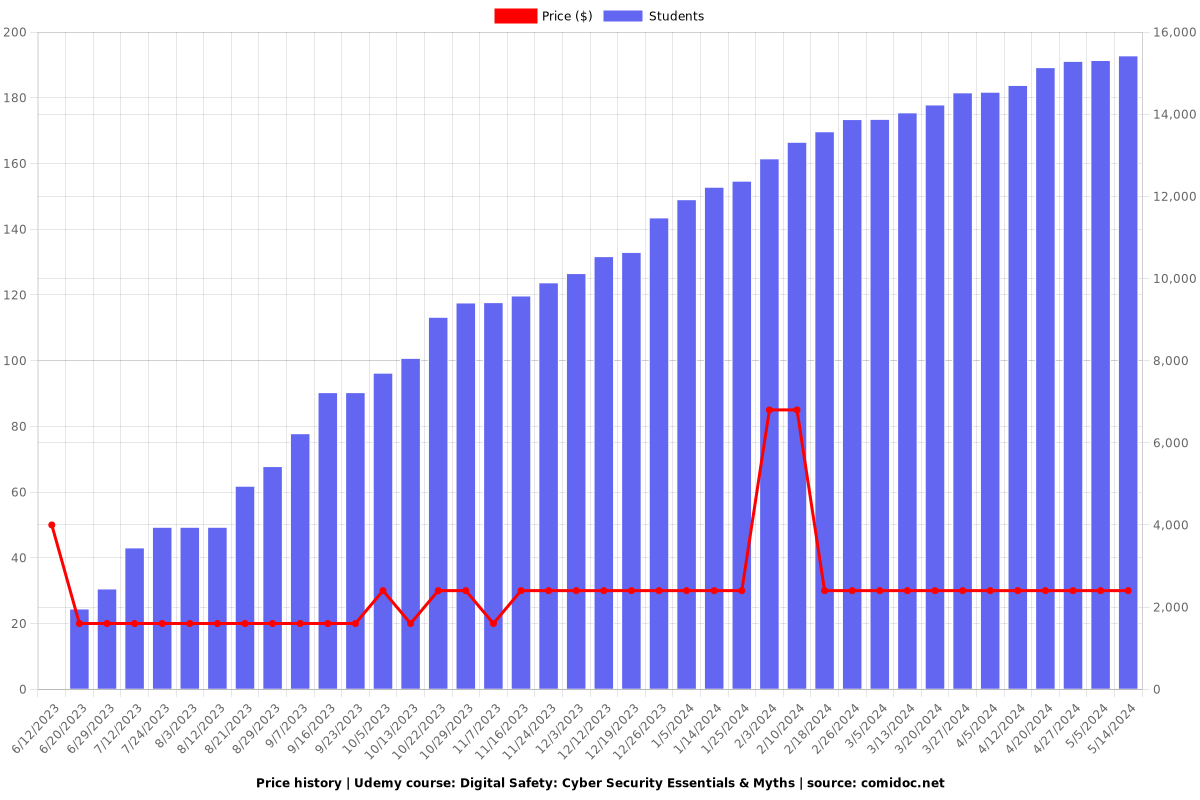
$29.99
regular price
What you will learn
The students will learn the best practices for securing personal and organizational data.
The students will gain a deep understanding of the importance of cybersecurity.
The students will learn about the various impacts and outcomes resulting from cyber attacks.
The students will gain essential knowledge about the different types of cybersecurity threats.
The students will gain understanding of various misconceptions about cybersecurity.
The students will understand that cybercrimes are committed for various reasons such as money, personal revenge, fun or recognition
The students will understand the importance of incident response plan in the context of cyber security.
Why take this course?
1. **Cybersecurity** is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks. These cyberattacks are usually aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information, extorting money from users, or interrupting normal business procedures.
2. **Phishing** is a deceptive attack technique used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. It occurs when an attacker, masquerading as a trusted entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message. The recipient is then tricked into clicking a malicious link, providing sensitive data, or downloading a virus.
3. **Cybercriminals are not solely outsiders**. In fact, the biggest threats can come from within an organization, from disgruntled employees, contractors, or business partners who have inside access to the network and its data. These insiders may exploit their privileged positions for various reasons, including financial gain, espionage, or personal revenge.
4. **Antivirus/anti-malware software** provide a first line of defense against known viruses and malware. However, they are not foolproof and cannot protect against zero-day threats (see below), advanced persistent threats, or social engineering attacks. Therefore, relying solely on antivirus software is not adequate for comprehensive cybersecurity.
5. **Changing passwords regularly** helps to mitigate the risk of unauthorized access in case a password is compromised. It's also important to use strong, unique passwords and employ multi-factor authentication where possible.
6. **Cybersecurity is not the responsibility of the IT Department alone**. It's a collective responsibility that involves everyone in an organization. Every user must adhere to best practices for cybersecurity.
7. **Incident response** is a structured approach, encompassing detailed plans and procedures with which organizations and individuals can effectively deal with actual or impending cyberspace security events. These activities enable the organization or individual to react and recover from cyber attacks or other adverse conditions affecting the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of computing assets.
8. **Compliance** in cybersecurity refers to the adherence to the required and recommended standards and regulations that govern data protection and privacy controls within an information system or organization. Non-compliance can lead to legal and financial penalties, loss of customer trust, and increased risk exposure for organizations and individuals.
9. **Encryption** is a process whereby data is encoded and then decoded for confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and data privacy protection purposes. Encryption techniques are used to secure data while being stored or transmitted over a communications network, such as the internet. Encryption is an essential security mechanism used in cybersecurity to protect sensitive information and data from unauthorized access by potential attackers or adversaries.
10. **Mobile Security** encompasses a series of policies, technologies, and configurations that are used to secure mobile devices (such as smartphones and tablets) from various cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks, such as malware, phishing scams, eavesdropping, interception, data breaches, man-in-the-middle (MitM), session hijacking, social engineering attacks, physical theft, and loss.
11. **Incident response plan** is a structured written plan that provides step-by-step detailed instructions and guidance on how to effectively react, handle, manage, contain, mitigate, recover from, and respond to actual or potential cybersecurity incidents and events within an organization or for an individual. The incident response plan includes procedures for different types of cyber incidents and events, such as malware infections, data breaches, denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, network security compromises, and other cyberspace security threats.
12. **Compliance with regulations** is critical because organizations must adhere to specific industry standards and governmental regulatory requirements to avoid legal consequences and penalties. These standards often involve regular updates and assessments of cybersecurity policies, procedures, controls, practices, and technologies to ensure ongoing compliance.
13. **Incident response team** typically includes representatives from IT, security, operations, legal, human resources (HR), public relations (PR), management, and other key departments within an organization. The incident response team works together collaboratively as a coordinated cross-functional interdisciplinary team to address, manage, handle, contain, mitigate, recover from, and respond to cybersecurity incidents and events.
14. **Remote tracking** is a feature that can be enabled in various devices, including smartphones and other mobile and IoT (Internet of Things) devices, to help locate the device if it is lost or stolen. It can also be used to remotely wipe data from the device if it falls into the wrong hands.
15. **Remote wiping feature** allows users to remotely clear, delete, or wipe all sensitive data, information, and contents from a mobile device if it is lost or stolen. This is an essential security feature for protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access in the event of loss, theft, or compromise.
16. **Data backup and storage** are critical security measures that involve regularly backing up and storing copies of all important sensitive data, information, and content in secure safe locations to prevent data loss and to allow for data recovery and restoration in the event of a cyber attack, data breach, natural disaster, or other adverse conditions.
17. **Firewall** is a network security device that monitors incoming and outgoing all network traffic and applies a set of rules at the boundary of a network, which are defined by the user to control what data and information can enter or leave. These rules serve to allow or block certain network traffic based on IP addresses, protocols, ports, and other criteria.
18. **Virtual Private Network (VPN)** provides a secure encrypted connection over a less secure network, such as the public internet, to enable users to safely and privately transmit and receive data, information, and communications without exposure to potential cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks. A VPN is an essential security tool for protecting sensitive data and information while traversing or traveling through potentially vulnerable networks.
19. **Intrusion Detection and Prevention System (IDPS)** monitors network and system traffic for signs of a potential intrusion attempt or actual attack and alerts the administrator so they can take appropriate actions to detect, prevent, block, mitigate, respond, and handle such cyber threats.20. **Web Application Security** involves implementing and enforcing a comprehensive series of security measures and controls designed to protect sensitive data and information on a web application from various forms of cyber attacks, including but not limited to XSS (Cross-Site Scripting), SQL injection, CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery), and other attack vectors.
These are just some of the many critical aspects of cybersecurity that need to be addressed and managed by organizations and individuals alike. Cybersecurity is a complex, multifaceted, and dynamic field that encompasses many different interrelated components, technologies, practices, protocols, policies, principles, standards, and regulations that all work together in concert to protect against a wide array of potential cyber threats, vulnerabilities, and attacks. It is essential for everyone to stay informed and educated about the importance of cybersecurity in order to safeguard sensitive data and information from various types of cyber risks and threats.
Reviews
Mayank
January 8, 2024
I found this course very valuable.
By taking this course i came to know about the deep detailing of Cybersecurity.
Umair
October 29, 2023
All the course was theory. I was actually looking for some practical work but the overall knowledge is well explained for beginners.
Victor
September 22, 2023
There’s a similar course by the same author, but this gives more in-depth knowledge of emerging trends as well as popular myths in world of cybersecurity
Sandeep
July 20, 2023
The course is unnecessarily lengthy. Lot of repetitions of same concepts. The English pronunciation of the narrator is very unusual. The course overall is valuable though.
John
July 13, 2023
I had great experience with you, I have learnt a lot for this course. I think from what I have acquired, I will put them into practice and help grow businesses. Thank you. I'm John from Ghana-West Africa.
Mohammed
July 5, 2023
The cyber security course provided valuable insights and practical knowledge that greatly enhanced my understanding of protecting digital assets and defending against cyber threats.
Torugbene
June 24, 2023
Cyber security is what everyone should be familiar with. Thanks for the educative and informative presentation
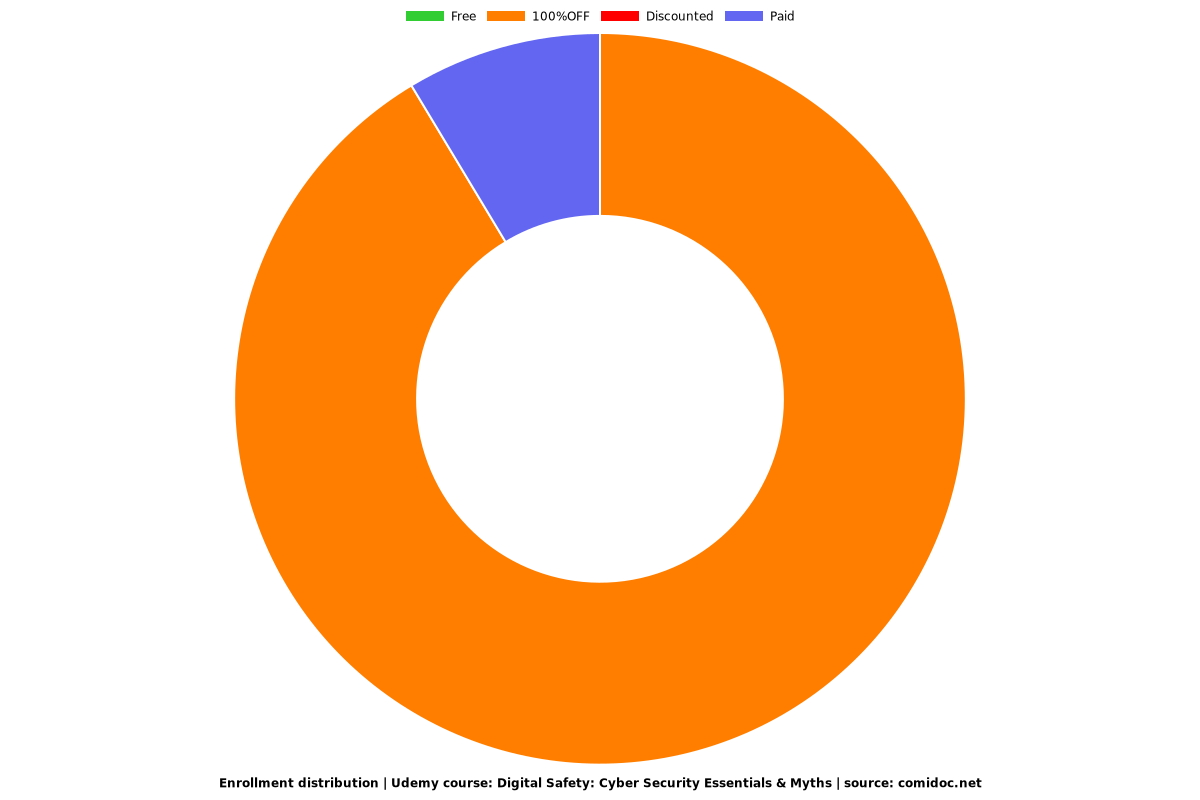
Charts
Price
Rating
Enrollment distribution
5376650
udemy ID
6/9/2023
course created date
6/12/2023
course indexed date
Prabh Kirpa Classes
course submited by